Cell 29, Baihuayuan, Panzhuang, Zhangdian, Zibo, Shandong, China
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-16 Origin: Site








Problems in the supply chain make people wait longer and pay more at auto body shops.
Aspect | Evidence | Significance |
|---|---|---|
Paints & Coatings Revenue | USD 59.82 billion in 2023 | Shows big part in auto body repair |
Adhesives Role | 3M makes special adhesives and sealants | Helps repairs get done faster and better |
Market Growth Drivers | Accidents, insurance, rules | Make more people need auto repair materials |
Good supply chains for paint, coatings, adhesives, and sealants are important. They help auto body repairs stay quick, safe, and high quality.
Steel and aluminum are used most in repairs. Each needs special tools and skills. This changes how much repairs cost and how long they take.
Advanced adhesives and sealants make repairs faster and stronger. Picking the right type is important. You must prepare surfaces carefully.
Problems in supply chains can cause delays. Raw material shortages and slow shipping raise costs for shops and customers.
New technology, lighter materials, and eco-friendly products are changing car repair. These help shops work better and protect the environment.
Auto body repair needs a steady flow of materials. Steel is in more than half of a car’s parts. The American steel industry makes strong steel for cars. Aluminum is used more now, especially in electric cars. Over 30 car models have more than 500 pounds of aluminum. The Aluminum Association says aluminum use is growing for doors and hoods. Steel and aluminum are both important for building cars today. OEM procedures tell shops how to use these materials.
Steel and aluminum are used most in auto body repair.
Steel is strong, lasts long, and is not expensive. Shops fix steel with welding and straightening.
Aluminum is light and does not rust easily. It helps cars use less gas and drive better.
Fixing aluminum needs special ways like riveting and bonding. Shops need special tools and training for this.
Steel repairs cost less and are easier to get done. Aluminum repairs cost more because they need advanced skills.
Steel keeps cars safe in crashes. Aluminum helps cars last longer by not rusting.
Each material needs different ways to fix it. These differences change how much repairs cost and how they are done.
Paint, coatings, adhesives, and sealants are also very important. Shops use them to make cars look good and stay safe. Adhesives and sealants help stick panels together and keep water out. Companies like 3M make advanced adhesives that help shops work faster and better.
Many people and companies help get repair materials to shops.
Product suppliers give shops parts, paint, coatings, adhesives, sealants, and other things they need.
Service channels include OE, DIY, and DIFM.
Sales channels sell new OEM parts, aftermarket parts, recycled parts, remanufactured parts, and salvage materials.
Auto body shops, both dealer and independent, fix cars with these materials.
Big companies like 3M, Axalta Coating Systems, LKQ Corporation, and Honeywell lead in making, researching, and selling these products. They spend money on new ideas and make better adhesives and sealants.
Online platforms and e-commerce make it easier to buy materials and help customers get what they need.
Training and certification groups like I-CAR make sure workers know how to fix cars the right way.
The auto industry works best when suppliers, shops, and tech leaders work together to keep repairs fast and reliable.
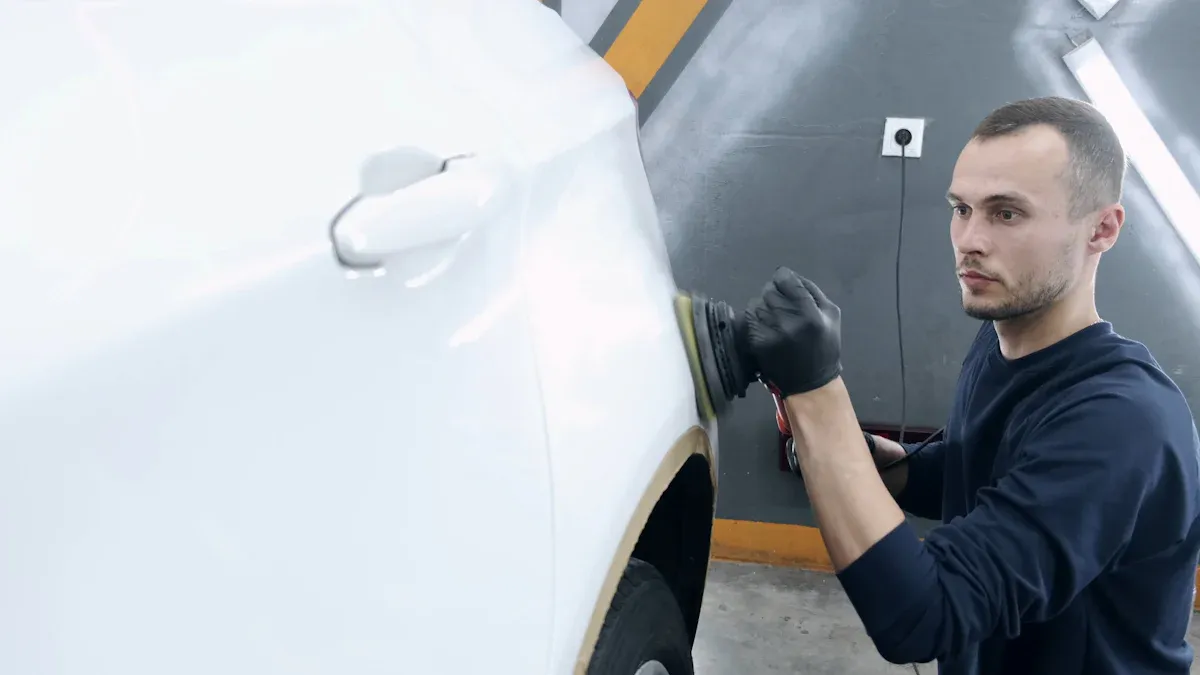

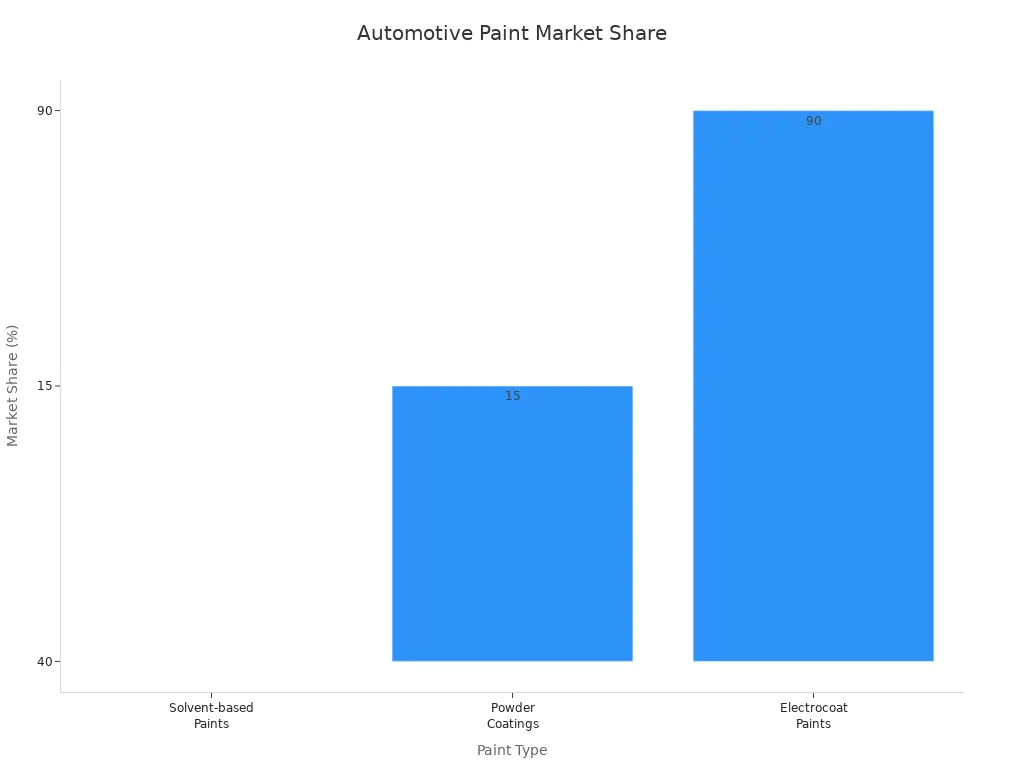
Auto body shops use different kinds of paint to fix cars. There are solvent-based paints, water-based paints, powder coatings, UV-curable paints, and electrocoat paints. Each kind helps in a special way. Solvent-based paints are used the most. They dry fast and last a long time. Water-based paints are getting more popular every year. Many shops pick them because they are better for the environment. Powder coatings are about 15% of the market. They help stop rust and damage from chemicals. UV-curable paints are used for fancy repairs. They dry right away when hit with UV light. This saves time and helps shops work faster. Electrocoat paints are used as primers on most new cars. Shops want to fix cars quickly and match colors well. So, they choose paints that are fast and look good.
Paint Type | Market Share / Usage | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Solvent-based Paints | Dominant due to durability and fast drying | |
Water-based Paints | Rapid growth with 5.2% CAGR | Favored for low VOC emissions |
Powder Coatings | ~15% market share | Excellent corrosion and chemical resistance |
UV-curable Paints | Significant in high-end applications | Instant curing under UV light |
Electrocoat Paints | Over 90% coverage in new vehicles (primers) | Widely used in primer applications |
Paint and coatings are very important in fixing cars. The clear coat is a see-through layer on top of the color. It keeps the paint safe from scratches and chips. It also blocks the sun’s rays, water, and dirt. This stops the paint from fading or peeling. The clear coat makes cars shiny and bright. It helps match colors when fixing spots. This keeps the car looking nice and keeps its value high. The clear coat also keeps dirt off, so cleaning is easier. When shops use coatings the right way, cars stay looking new for a long time. Good paint and coatings help cars look great and last longer, even after big repairs.
Adhesives are very important in fixing cars. Technicians pick different adhesives for each job. Each one helps in its own way. The table below shows the main types and what they do:
Adhesive Type | Advantages |
|---|---|
Urethane | Flexible, moisture-curing, ideal for windshields |
Acrylic | Fast curing, works well with plastics |
Epoxy | Strong, versatile, perfect for structural repair |
Polyurethane | Durable, flexible, bonds materials with different expansion rates |
Silicone | Waterproof, temperature resistant, used for sealing |
Cyanoacrylate | Quick fixes, best for small repairs |
Cyanoacrylate adhesives are good for quick, small repairs. They are not strong enough for big jobs.
Silicone adhesives and sealants keep out water and heat. They are great for stopping leaks around doors and roofs.
Urethane adhesives make a tight seal for windshields.
Epoxy adhesives are very strong. They are best for metal parts and big repairs.
Polyurethane adhesives stick body panels together. They make the car look smooth with no bolts showing.
Acrylic adhesives fix plastic parts fast. They dry quickly so repairs go faster.
Getting the surface ready and picking the right adhesive is important. High-performance adhesives need careful use and the right drying time.
Adhesives and sealants help with many car repairs. Automotive adhesives and sealants help cars look and work like new. The table below shows how each adhesive is used and why it works well:
Adhesive Type | Application in Repair | Key Properties Supporting Use |
|---|---|---|
Urethane Adhesive | Bonding metal/plastic, filling holes or cracks | Flexible, strong, weather resistant |
Polyurethane Adhesive | Emergency repairs on wet surfaces | Maintains strength even when wet |
Epoxy Adhesive | Underbody and corrosion-prone area repairs | Strong, corrosion resistant |
Acrylic Adhesive | Cosmetic repairs, quick setting, paintable | Fast cure, UV resistant |
Sealants stop water and air from getting inside the car. They protect the inside and the body panels. Automotive sealants and adhesives also help attach trim, glass, and panels. High-performance adhesives let cars be lighter and repairs go faster. Technicians use these products to keep cars safe and do a good job.
Using the right adhesives and sealants makes repairs better, saves money, and gets cars fixed faster. Shops that use advanced automotive adhesives and sealants do a better job than others.

Raw material shortages have caused big problems for auto body repair. Paint, coatings, adhesives, and sealants all need certain chemicals and minerals. If these materials are hard to get, everything slows down. Some recent events made shortages even worse:
Poly(vinylidene)difluoride (PVDF) resin was very hard to find in 2021 and early 2022. Prices went up by 200-300% because more was needed for batteries and semiconductors.
Titanium dioxide is important for paint. The war between Russia and Ukraine made it hard to get. This made prices go up.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a two-year problem for supply chains. Fewer companies made raw materials, so prices rose and wait times got longer.
Petrochemical prices changed a lot and shipping was slow, especially in the Middle East. This made it even harder for manufacturers to get what they needed.
From late 2019 to 2022, the cost of raw materials for coatings went up by 40-50%. This made it hard for companies to know costs and keep up with orders.
In 2023, shops still had trouble getting alkyd resins and some additives. Prices started to settle, but supplies were still low.
The coatings industry has had these problems for years. Global supply chains are complicated, so it is hard to fix things fast. Now, companies try to lower risk by using more suppliers, making products closer to home, and using new technology.
When there are not enough raw materials, shops wait longer for paint, adhesives, and sealants. This makes repairs take more time and cost more for everyone.
Problems with logistics and distribution also make it hard to get repair materials. Many shops say they have to wait for paint and adhesives. In the last two years, 61% of people at the Collision Industry Conference said they had trouble getting parts and materials. Shops often do not know when their orders will come. Different ordering systems from many companies and insurers make things confusing and slow.
Returning broken or wrong parts takes a lot of time and can cost extra money. New rules from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and special certifications make ordering even harder. These problems make repairs take longer and make customers less happy.
Some companies have found new ways to help. Toyota Logistics Services uses computers to track repair times and find delays. New repair methods like paintless dent repair (PDR) help shops work faster and use fewer delayed parts. Companies like Selsystem and Ballsystem use PDR to fix big damage quickly, even when other materials are late.
Shops now use digital color matching and machines to mix paint. This saves time and cuts down on waste. These tools help keep repairs good, even when paint and resin are late.
Rules and laws are very important for the supply chain of adhesives, sealants, and coatings. Wars, like the one between Russia and Ukraine, make trade harder and make it tough to get things like titanium dioxide. Political problems between Western countries and Russia or China can change trade rules and make supplies less steady. Slow economies in places like China also make the supply chain weaker.
Many countries now have rules for chemicals in adhesives and sealants, like PFAS, to keep people and the planet safe. These rules can limit what companies can use. Worries about climate change have led to stricter rules for emissions and waste. For example, there are now limits on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in paint and adhesives. This makes companies create more eco-friendly products.
Changes in oil and gas prices affect the cost of coatings and adhesives. If Brent crude oil goes up by $10, coating makers pay 3% more. This makes it hard for companies to plan and keep prices steady.
Environmental rules and people wanting greener products also change the market. Companies now work on making bio-based and waterborne coatings and adhesives. Governments want products that help recycle cars and make them safer to throw away. These changes make companies invent new things while following strict rules.
Companies like 3M are leading by making new adhesives and sealants that are good for the environment and work well. Their strong supply chains help shops get what they need, even when times are tough.
The auto collision repair market is changing a lot. Shops and car makers now use more lightweight materials. This helps cars use less gas and pollute less. It also makes cars drive better. Car makers mix different materials to make cars strong but not heavy. Some common lightweight materials are:
Aluminum alloys are used for body panels, engine blocks, and wheels. Half of North American cars have aluminum hoods. By 2025, this could be 80%.
Advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) are lighter than regular steel. They save 20-25% in weight. These steels let makers use thinner parts that are still strong.
Carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) are very strong and light. They are mostly in fancy and electric cars because they cost a lot.
Magnesium alloys are 75% lighter than steel. They are used in sports cars and some inside parts. But they can break easily and rust.
Titanium alloys are rare. They are strong and light for special uses.
These materials help cars stay safe and weigh less. In 2024, the world market for lightweight car materials was over $93 billion. This number keeps growing. Composites are popular because they do not rust and work well. Europe uses these materials the most. Asia Pacific is starting to use them more too.
Repair shops must learn new ways to fix these cars. They need new tools and training for lightweight materials. Old repair methods do not always work on aluminum or carbon fiber. Shops use special adhesives and coatings to fix and protect these materials. Electric cars also need special adhesives for high voltage and heat. As more electric cars come out, shops must learn new repair skills and use new materials.
Technology is changing how shops fix cars. Shops use robots, smart tools, and computers to work faster and better. Some important new technologies are:
Robots help with welding and painting. This makes repairs faster and the same every time.
Advanced diagnostic tools connect to car computers. They help find problems quickly and correctly.
3D scanners and computer systems measure cars in detail. This helps fix cars so everything fits right.
AI tools help check damage and give repair estimates faster.
Laser measuring tools and automatic sanders make work easier and quicker.
AI quality control systems find tiny mistakes. This makes sure repairs are done right.
3D printing lets shops make new parts when they need them. This helps when parts are hard to find.
Cloud-based diagnostics let shops see car data right away. They can get ready for repairs before the car comes in.
Electric cars and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) need special tools and training. Shops must set up sensors and fix tricky electronics safely. Training programs like I-CAR help workers learn new repair skills.
These new tools cost money, but they help shops fix cars faster and better. Customers are happier and shops can beat their competition by using new technology.
Sustainability is very important in car repair now. Shops and car makers want to help the environment and still do good work. Some trends in this area are:
The industry is switching from solventborne coatings to water-based paints. Water-based paints make less air pollution and still look good.
Shops use recycled and reused parts to make less waste and save resources.
Eco-friendly adhesives made from green materials are used more. These adhesives are safer for the planet.
Energy-saving equipment like LED lights and better spray booths use less power.
Many shops put up solar panels to use less fossil fuel.
Better waste management, like recycling and safe disposal, helps protect nature.
Paintless dent repair (PDR) means less repainting. This is better for the environment.
Digital tools help shops use less paper and order parts smarter. This cuts down on shipping pollution.
Smart coatings can heal themselves and stop rust. These coatings help cars last longer and need fewer repairs. Powder coatings are getting more popular. They have little or no VOCs and protect cars from rust. Big companies spend money on better powder coatings that use less energy and work better.
The market for green adhesives and coatings will keep growing. By 2032, the market for car coatings could be over $57 billion. Adhesives and sealants are also growing because of electric cars and lighter cars. As rules get tougher and people want greener products, shops and makers must keep inventing new things.
Sustainability, new technology, and lightweight materials are changing car repair. Shops that follow these trends will do better, make customers happy, and help the planet.
When the supply chain has problems, repair shops and customers are affected. If shops cannot get paint, adhesives, or sealants, repairs slow down or even stop. Many shops say old equipment and missing parts make it hard to finish repairs on time. Mistakes from tracking by hand and not having good computer systems cause more delays. This means repairs pile up and take longer. Shops have more downtime and cannot fix cars as quickly. The quality of repairs goes down when these problems happen. More mistakes mean more wasted materials and machines do not work as well. When repairs are late, both shops and customers get upset. It becomes harder for shops to do a good job.
Shops need to watch their supplies closely to avoid delays and keep repairs good.
When the supply chain has problems, shops cannot get spare parts. This can stop work and slow down repairs.
Old equipment makes things worse because parts are hard to find. New technology does not fit, so machines break more and repairs are not as good.
Problems with tracking and not using good systems cause more delays.
Shops say machines are down longer and repairs take more time because parts are missing.
All these problems together mean more waste, slower machines, and missed deadlines.
Repair shops are paying more because of supply chain problems. Paint and other supplies now cost a lot more. In early 2025, paint and material prices went up by 7.4%. Since 2020, prices have gone up almost 60%. Shipping is slower, and new rules and missing materials make things cost more. Not enough workers and higher pay also add to the cost. Some parts, like bumpers and headlights, now cost almost twice as much. Because of this, shops must charge more for repairs. Customers see higher bills and pay more for insurance. Since 2020, car insurance has gone up by 36%. This is because repairs cost more. Many people now pick cheaper parts, which changes what shops buy and use.
Shops and makers use different ways to handle supply chain problems. They keep good records of damage and repairs to help with insurance and show what was done. Shops watch which parts they use most to guess what they will need. Many shops keep extra parts that are used a lot or are hard to find. They ask suppliers for faster delivery to get paint, adhesives, and sealants on time. Some shops share parts with other shops nearby to avoid waiting. New computer tools help shops track supplies and spot problems quickly. Makers also keep extra important parts, use more than one supplier, and save space to make things when needed. These ideas help shops get the materials they need and keep working even when the supply chain is slow.
Shops that use these ideas can give better service, save money, and keep up with changes in car repair.
Supply chain problems have changed how car repairs are done.
Parts now cost 8% more, and repairs take longer.
Repairs are harder and need more parts, so costs go up and people wait more.
Shops and makers can lower risks by keeping better track of parts, working together in teams, and learning from experts and schools. The car repair market is changing with new materials, computers, and green ideas. In the next five years, online shopping and better delivery will make the supply chain faster and smarter.
Problems in the supply chain, not enough raw materials, and slow shipping often make things late. Shops sometimes have to wait longer for paint, coatings, or adhesives. These problems can make repairs take more time and cost more for everyone.
Technicians pick products by looking at what the car is made of, what kind of repair is needed, and what the manufacturer says to use. Big companies like 3M and Axalta make special products that help shops do strong repairs that last and follow the rules.
Yes. Water-based paints let out fewer bad chemicals into the air. Many shops use them now to follow environmental rules and help stop pollution.
Shops watch their supplies carefully, use computers to order, and work with suppliers they trust. Some shops keep extra stock of things they use a lot. These actions help stop delays and keep repairs on time.
Material prices go up, there are not enough workers, and new rules make things cost more. Insurance prices also go up because of this. Customers may have to pay more for repairs and insurance.